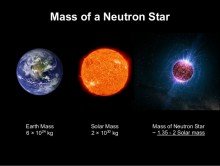
When the core of a large star (one that is about 10-29 times the mass of our Sun) collapses, it forms one of the smallest and densest stars that we know of. A neutron star. They are usually around 20km in diameter with a mass that is approximately twice that of our Sun. And as the illustration suggests, a thimblefull here on Earth would weigh about as much as an entire mountain.
So where do they come from? Well, when a massive star comes to the end of its life it can create a huge explosion called a supernovae. The light from a supernovae can sometimes be so bright as to outshine an entire galaxy. What is left undergoes gravitational collapse, squeezing the remaining core down to a small neutron star, which is thought to be made almost entirely of neutrons.
It’s interesting to note that some of these neutron stars will collapse even further to form black holes.
Graham Foster
Founder of Mind Rocket.
View the original article here.
Visit www.mindrocket.co.uk for more amazing science facts.
Also please Like the Mind Rocket Facebook page to get science facts every day.