This article will investigate how Zionist Jews are attracting hostility and why we must not succumb to antisemitism.
What is Zionism?
Zionism is a political and ideological movement that emerged in the late 19th century, with the primary goal of establishing and supporting a Jewish homeland in the historic region of Palestine, which is now the modern state of Israel. The term “Zion” is often used in reference to Jerusalem, a significant city in Judaism.
Key aspects and goals of Zionism include:
- Jewish self-determination: Zionism advocates for the right of Jewish people to have a sovereign and independent state where they can determine their own political, social, and cultural destiny.
- Return to the historic homeland: Zionists believe in the importance of Jewish people returning to their ancestral homeland, which is deeply rooted in Jewish religious and historical traditions.
- Jewish national identity: Zionism seeks to strengthen and promote a collective Jewish national identity, which had been weakened in the diaspora (the dispersion of Jews throughout the world).
- Political and diplomatic efforts: Over the years, Zionists have pursued political and diplomatic means to establish and maintain the State of Israel. This included lobbying international powers and institutions.
Zionism has several ideological and political branches, ranging from religious and conservative to secular and progressive. The movement has been associated with various leaders, including Theodor Herzl, who is often considered the father of modern political Zionism.
What is Judaism?
Judaism is one of the world’s oldest monotheistic religions, with a rich history and diverse traditions. It is the religious and cultural tradition of the Jewish people. Here are some key aspects of Judaism:
- Monotheism: Judaism is centered around the belief in one God, who is considered the Creator of the universe and the source of moral and ethical guidance. This monotheistic belief is one of the defining features of Judaism.
- Sacred Texts: Judaism places great importance on its sacred texts. The Torah, which consists of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible (Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy), is the central religious text. Additionally, there are other important texts, like the Talmud and various commentaries.
- Covenant: Judaism emphasises the idea of a covenant, a sacred agreement or contract, between God and the Jewish people. The covenant includes moral and ethical principles as well as specific commandments (mitzvot) that guide Jewish life.
- Synagogue Worship: Jewish worship and religious study often take place in synagogues, which are communal places of prayer and study. The Jewish Sabbath (Shabbat) is observed from Friday evening to Saturday evening, with special services and rituals.
- Holidays and Festivals: Judaism has a calendar filled with religious holidays and festivals, including Passover, Yom Kippur, Rosh Hashanah, and Hanukkah. Each of these occasions has its own traditions, rituals, and significance.
- Kosher Dietary Laws: Observant Jews adhere to kosher dietary laws, which specify what foods are permissible to eat and how they should be prepared. These laws are based on the Torah and have religious and cultural significance.
- Ethical and Moral Principles: Judaism places a strong emphasis on ethical and moral behaviour, including principles of justice, charity (tzedakah), and the pursuit of righteousness (tikkun olam), which means repairing or improving the world.
- Diverse Traditions: There are various branches and denominations within Judaism, including Orthodox, Conservative, Reform, and Reconstructionist Judaism, each with its own interpretations and practices.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Judaism has had a profound influence on the development of Western civilisation and Jewish culture has contributed to art, literature, science, and other fields.
It’s important to note that there is a great deal of diversity within the Jewish community, and individual beliefs and practices can vary. Judaism is not only a religious tradition but also a complex cultural and historical heritage that has evolved over millennia.
Zionist Jews
“Zionist Jews” are Jewish individuals who support the ideology of Zionism, which is the political and national movement that advocates for the establishment and maintenance of a Jewish homeland in the historic region of Palestine, which is now the modern State of Israel. These individuals believe in the importance of Jewish self-determination and the return of Jewish people to their ancestral homeland.
Are the following views acceptable or unacceptable?
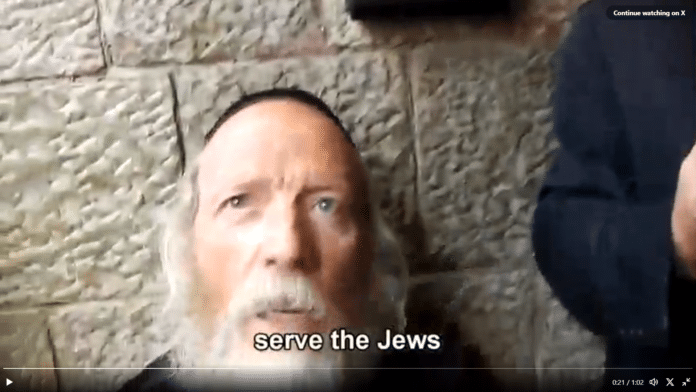
???????????? Shocking attitudes from these Zionists. Have we in the west been allowing Jewish extremism to flourish?
— Carl (@CarlEckett) November 3, 2023
“God made them [the non jews], to serve the Jews.
All the billions of non jews you see around the world, they are just for the jews benefit”
pic.twitter.com/hCMNbHDNr2
The feeling of superiority and dogma amongst these men is personally sickening. They are a cause of hate and division. However, we must not succumb to antisemitic hate or respond to those who shout ‘antisemitism’ when it does not exist. They are just as guilty of the same hate and division and do it because they fear critique. Interestingly, many will say they support free speech.
What is antisemitism?
Antisemitism is a term used to describe prejudice, discrimination, hatred, or hostility directed toward Jewish people based on their real or perceived Jewish identity. It has a long and troubling history, spanning centuries and various regions of the world, and has taken many different forms.
Antisemitism can manifest in a range of ways, including:
- Stereotyping: The use of harmful stereotypes about Jewish people, such as portraying them as greedy, manipulative, or conspiratorial.
- Discrimination: Unfair treatment of Jewish individuals in various aspects of life, including employment, housing, education, and social interactions.
- Hate speech: The use of offensive language or rhetoric that promotes hatred, prejudice, or violence against Jewish people.
- Violence and hate crimes: Physical attacks or acts of violence directed at Jewish individuals or Jewish institutions, motivated by antisemitic beliefs.
- Conspiracy theories: The spread of false and harmful conspiracy theories that blame Jewish people for global problems or events.
- Holocaust denial: Denying or distorting the historical reality of the Holocaust, in which millions of Jews were systematically murdered by the Nazis during World War II.
Antisemitism has had devastating consequences throughout history, culminating in the Holocaust, one of the most heinous acts of genocide in the 20th century. In the aftermath of the Holocaust, there has been a global commitment to combat antisemitism and promote tolerance and understanding.
Efforts to address and counter antisemitism include educational initiatives, legal protections against hate crimes, and advocacy for interfaith dialogue and understanding. Many countries have laws in place to prohibit hate speech and discrimination based on religious or ethnic identity, including antisemitism.
It’s important to recognise and reject antisemitism, no matter the provocation by some, as well as to promote tolerance, diversity, and understanding among all communities and religions.
Douglas James
If you would like your interests… published, submit via https://dorseteye.com/submit-a-report/
Join us in helping to bring reality and decency back by SUBSCRIBING to our Youtube channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCQ1Ll1ylCg8U19AhNl-NoTg SUPPORTING US where you can: Award Winning Independent Citizen Media Needs Your Help. PLEASE SUPPORT US FOR JUST £2 A MONTH https://dorseteye.com/donate/