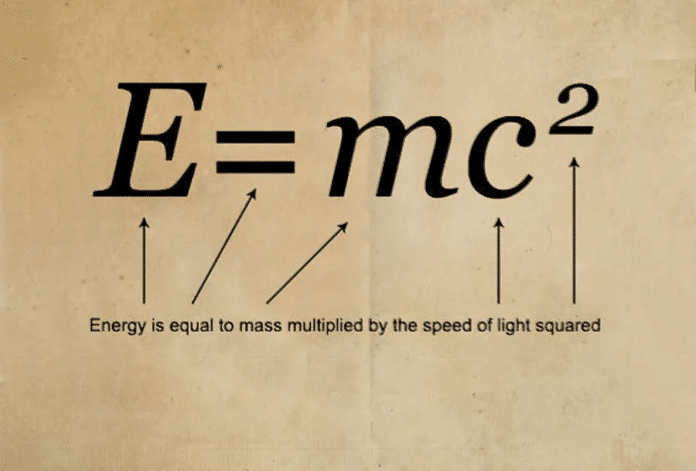For those who like things simple.
E=MC² is an equation derived by Albert Einstein in his theory of special relativity. The equation shows the relationship between mass (M) and energy (E) and is represented by the constant squared speed of light (C²).
The equation states that the energy (E) of an object is equal to its mass (M) multiplied by the speed of light (C) squared. This means that any object with mass has an inherent amount of energy that is proportional to its mass. The speed of light is an incredibly large number, so even a small amount of mass can correspond to a very large amount of energy.
In practical terms, this equation has significant implications in fields such as nuclear physics, where it explains the energy released during nuclear reactions. It also underpins the development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons.
Overall, E=MC² is one of the most famous equations in physics and has helped scientists to better understand the relationship between mass and energy in the universe.
Join us in helping to bring reality and decency back by SUBSCRIBING to our Youtube channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCQ1Ll1ylCg8U19AhNl-NoTg and SUPPORTING US where you can: Award Winning Independent Citizen Media Needs Your Help. PLEASE SUPPORT US FOR JUST £2 A MONTH https://dorseteye.com/donate/