Virtual private networks help us to enjoy a safer internet experience and to access content without restrictions. But like with any technology, VPNs still have moments of weakness.
The prospect of sluggish speeds, frustrating crashes and limited levels of access, some VPNs can be highly problematic at times when you may need them the most.
(Image: Statista)
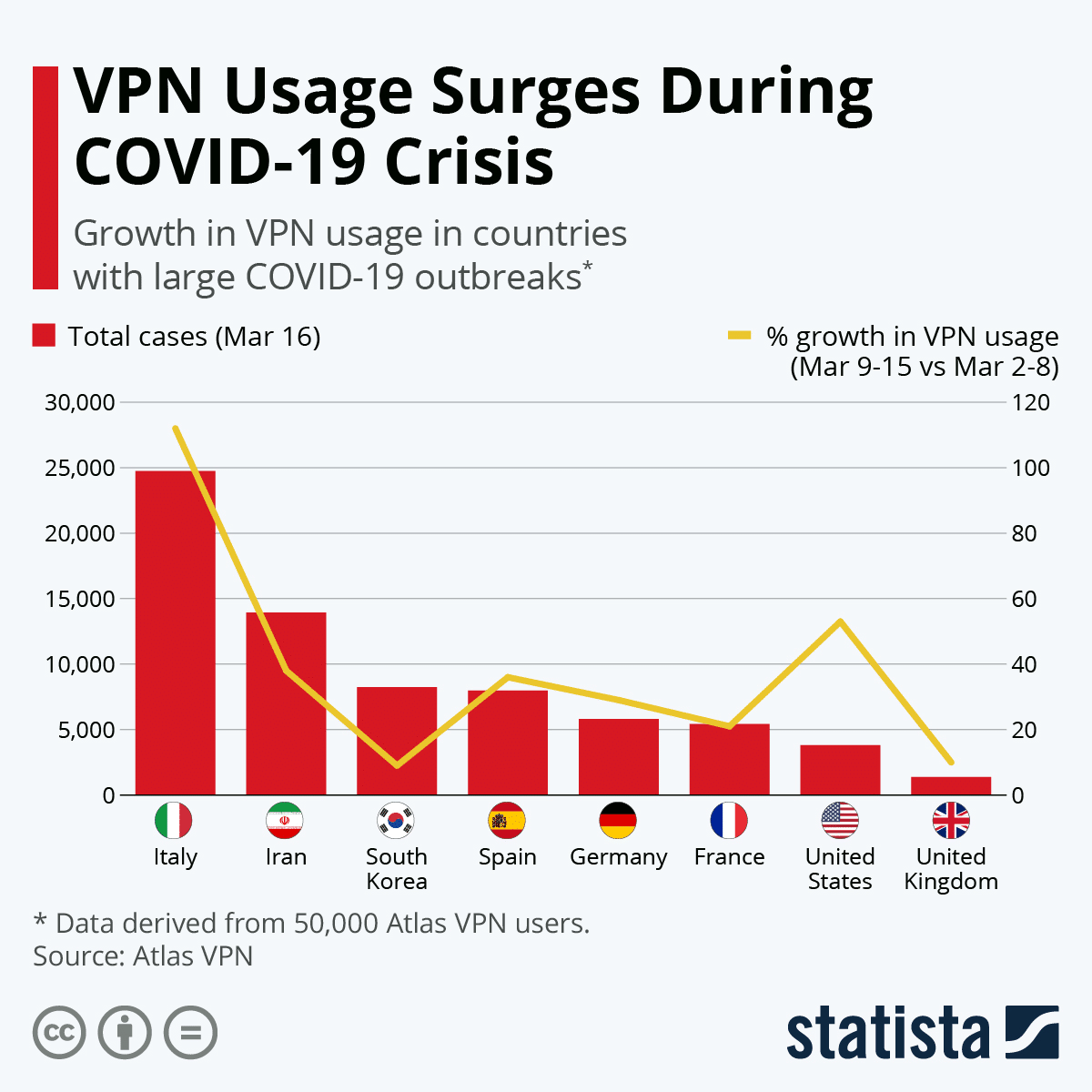
Despite their drawbacks, VPN usage has grown significantly in the wake of the COVID-19 outbreak. As more businesses switch to operating on a more remote basis, virtual private networks help to keep confidential information safe online where employees are operating outside of the office.
As the popularity of VPNs continue to gather momentum, let’s explore three of the key reasons why the technology doesn’t always work:
1. Your VPN Connection May Have Been Rejected
Having a VPN client’s connection rejected is possibly the most common problem to run into. Part of the reason for this issue is that there are a lot of scenarios that can come into the mix that can lead to a connection rejection. If your VPN server is rejecting client connections, the first thing you should do is check that your Routing and Remote Access service is running. You can check this by opening the server’s Control Panel and clicking on Administrative Tools, followed by Services.
Once you’ve verified that the necessary services are up and running, try pinging the VPN server by IP address from your VPN client. You’ll need to ping by IP address initially as a means of verifying that your basic connectivity is functioning. If the ping works, set up another ping to the server, but this time ping by the server’s fully qualified domain name, as opposed to its address. If this ping doesn’t work, you have a DNS problem, because the client is unable to resolve the server’s name to an IP address.
If your connection is still getting rejected, it may be that you’re suffering from authentication issues. For more complex rejections, many reputable VPN providers offer strong levels of customer support to help with this form of troubleshooting. After all, your VPN service doesn’t count for much if it’s unable to get off the ground.
2. VPNs May Make Your Internet Extremely Slow
Your VPN will always make your internet connection slower. This is due to the extra layers of security that need to be fixed onto your existing network. But they shouldn’t prompt a significant drop in speed. If your connection becomes so slow that it’s making it difficult to use, you’ll need to take decisive action.
Don’t worry, issues with VPN speeds can be common, and they may be solved fairly easily. Firstly, check the quality of VPN that you’re using. While many free services promise fast connections, this isn’t always the case. If a provider promises a quality of service that seems too good to be true, it probably is.
The server that you use for your VPN connection can also make a big difference when it comes to connection speeds. The closer you are to a server, the better speeds you’ll get as a result. You may also see improvements in speeds of servers that aren’t being used as much.
3. Some VPN Connections are Prone to Disconnecting
If your VPN client successfully connects before regularly disconnecting, this can be a significant nuisance – especially if you’re using a VPN for the purpose of remote work. These drops can also lead to significant security threats too – so it’s important that you work to mitigate these occurrences where possible.
Firstly, it may be an issue with your VPN server which is easy enough to address – simply find a server that’s closer or less congested with users and it may resolve the problem entirely.
Another approach is to disable your device’s firewall. While firewalls can form essential security barriers, they can also sometimes affect the connectivity of VPNs. Most of them can contribute to slowing your internet connection in a way that causes your internet to disconnect.
Depending on how you’re using your VPN, it could be useful to disable your firewall and rely purely on the level of security and privacy your VPN offers your browser.
If the problem persists, try checking your DNS server to see if the issue is emanating from there. VPNs supply their own DNS services when connecting but that doesn’t mean that it can’t mess with your connection. Different VPN providers offer varied requirements for altering DNS server settings including the commonplace ‘only use VPN DNS servers when connected.’
VPNs may offer an exceptional level of security that can bring essential layers of privacy to companies looking to operate in a more remote manner, or for individuals aiming to keep their private information safe online. However, keeping your connections secure can lead to problems depending on your ISP, device, firewall settings and router – so you may find yourself troubleshooting as you familiarise yourself with your VPN provider.
However, most of the time VPN customers can enjoy a strong and relatively speedy connection that they’re satisfied with – making the service ideal in a world that’s become significantly more remote in the wake of the pandemic.
PLEASE SUPPORT US FOR JUST £2 A MONTH